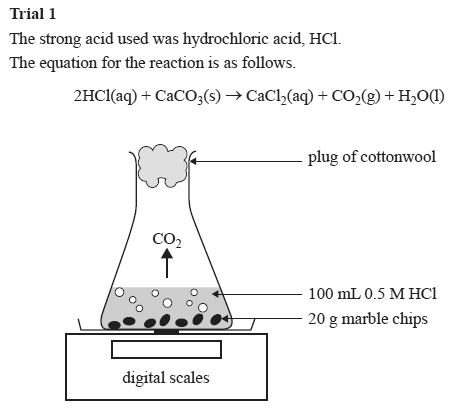
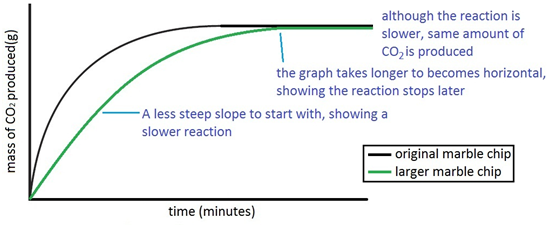
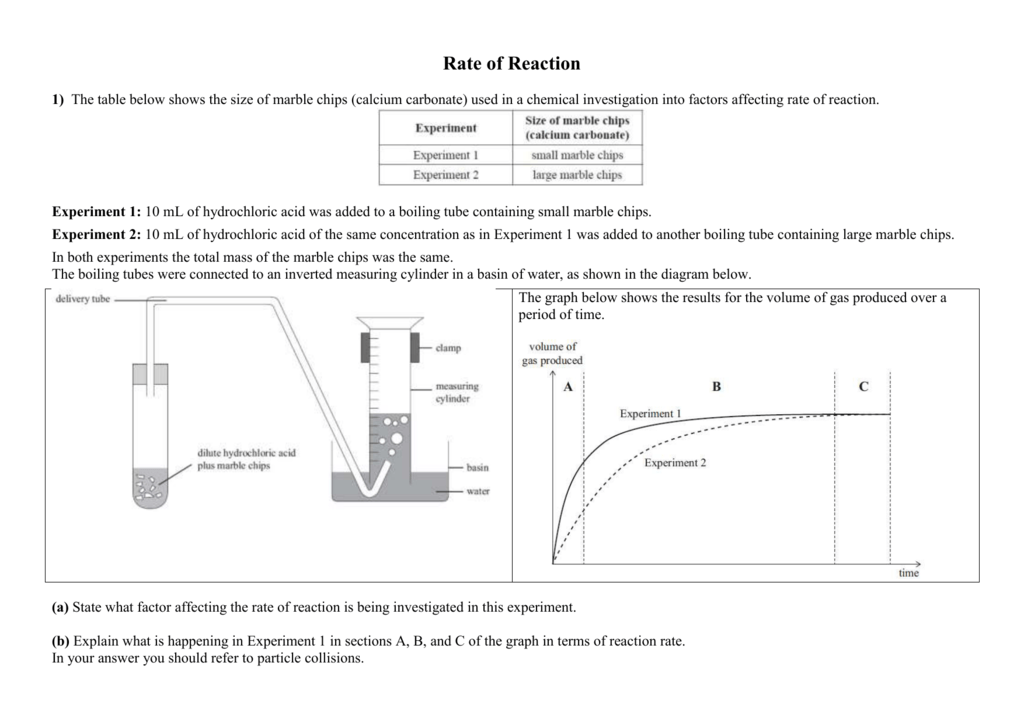
Marble chips and hydrochloric acid planning aim to find if changing the concentration of an acid will increase or decrease the rate of the reaction when marble is dissolved in hydrochloric acid.
Marble hcl reaction.
Pieces of marble are thrown into hydro chloric acid.
Marble reaction with hydrochloric acid drop a small amount of dilute hydrochloric acid on an area of your sample that has been scratched by a nail.
Marble is calcium carbonate and thus behaves in the same way.
The reaction takes place spontaneously.
The increased h increases the rate of the reverse reactions forming carbon dioxide and water.
Calcium carbonate is dissolved by hydrochloric acid thereby forming gaseous carbon dioxide.
With the equation caco3 2hcl cacl2 h2o co2 hypotheses a reaction occurs when particles collide.
Marble is crystalized caco3.
Being alkaline it reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce calcium chloride water and carbon dioxide.
This process is based on random particle movement.
Calcium carbonate and hcl.
The overall reaction is 2hcl caco3 cacl2 co2 h2o.
Hydrochloric acid marble chips the experiment the aim of this experiment is to find out how different variables affect the rate at which the reaction between marble chips caco and hydrochloric acid hcl takes place.
There are many variables that affect.
Therefore resulting in a quicker reaction.
Click each image to see positive and negative results of the acid test.
In fact if you take baking soda which contains hco3 and add vinegar which donates h to the solution this is precisely what happens.
This is because there will be more hydrochloric acid particles to collide with the marble chip particles.
Hydrochloric acid or hcl is a strong acid that donates h to water.
Marble chips are mostly made up of calcium carbonate which is a alkaline compound.
The combined reactants have a higher chemical potential than the combined products i e.
Caco3 s 2hcl aq 61614.
The higher the concentration of hydrochloric acid in the beaker the faster the reaction will take place.